Cardiac Troponin I (cTnI): A Breakthrough Biomarker in Cardiac Diagnostics
Introduction:
The field of biomedical diagnostics has witnessed remarkable advancements over the years, and one of the most significant breakthroughs in recent times is the utilization of Cardiac Troponin I (cTnI) as a diagnostic biomarker for cardiac-related conditions. This remarkable protein has revolutionized the way healthcare professionals diagnose and manage cardiac events, setting a new standard in precision and accuracy.
The Importance of Cardiac Troponin I (cTnI):
cTnI is a specific protein found in cardiac muscle cells, making it an ideal biomarker for assessing cardiac damage. When heart muscle is injured, whether due to a heart attack (myocardial infarction) or other cardiac conditions, cTnI is released into the bloodstream. Detecting elevated levels of cTnI in blood samples can indicate cardiac injury with remarkable sensitivity, even in cases where other cardiac biomarkers may remain unchanged.
The Diagnostic Process:
The diagnostic process involving cTnI typically begins when a patient presents with symptoms suggestive of cardiac distress, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or discomfort in the chest area. Healthcare professionals will order blood tests to measure the concentration of cTnI in the patient's bloodstream.
The Advantages of cTnI in Cardiac Diagnostics:
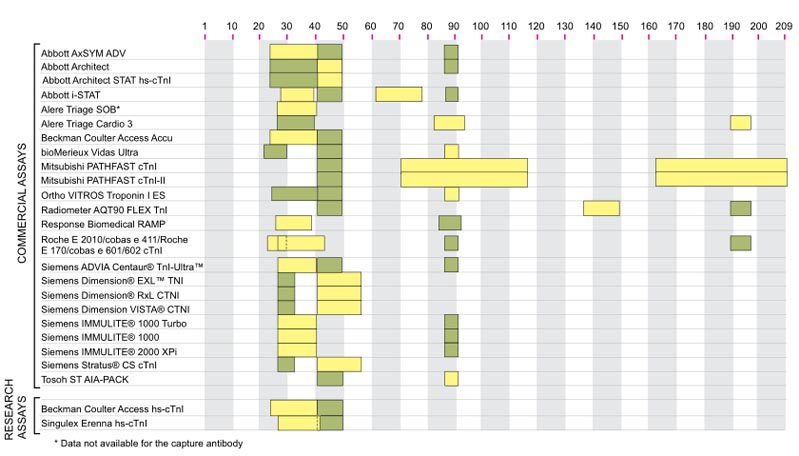
Sensitivity and Specificity: cTnI's exceptional sensitivity allows for the detection of even minor cardiac injuries. Moreover, its specificity to cardiac muscle ensures that elevated levels are highly indicative of cardiac issues, minimizing false positives.
Early Detection: cTnI can be detected within a few hours of a cardiac event, allowing for early intervention and treatment. This rapid detection significantly reduces the risk of complications and improves patient outcomes.
Monitoring: cTnI levels can be monitored over time to assess the progression of cardiac conditions and the effectiveness of treatment. This longitudinal data aids healthcare providers in making informed decisions about patient care.
Risk Stratification: The quantification of cTnI levels can help stratify patients into different risk categories, guiding the intensity of treatment and the need for additional diagnostic tests.
Reducing Unnecessary Procedures: cTnI's reliability in diagnosing cardiac events reduces the need for invasive and costly diagnostic procedures, such as coronary angiography, in cases where a cardiac event is unlikely.
Conclusion:
Cardiac Troponin I (cTnI) has transformed the landscape of cardiac diagnostics in the biomedical industry. Its remarkable sensitivity, specificity, and early detection capabilities make it an invaluable tool for healthcare professionals in diagnosing and managing cardiac-related conditions. As research continues to refine our understanding of cTnI and its applications, it holds the promise of further enhancing patient care and outcomes in the field of cardiology. This breakthrough biomarker exemplifies the potential of biomedical science to make significant strides in improving human health and well-being.
Related Immunoassays
- Cardiac Markers
-
Tumor Marker
-
PGII
-
G17
- CA50
-
CA125
- CA242
-
CA15-3
- CA19-9
- CA72-4
-
Pepsinogens I (PGI)
-
Human Epididymis 4 (HE4)
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
- Neuron-Specific Enolase (NSE)
- Cytokeratin 19 Fragment (CYFRA21-1)
- Human Progastrin-releasing Peptide (ProGRP Tumor Marker)
- Protein Induced by Vitamin K Absence or Antagonist-II (PIVKA II Tumor Marker)
- Alpha-fetoprotein(AFP)
-
CEA
-
Human Chitinase 3-like 1
-
PGII
- Inflammatory Marker
- Infectious Disease
- Hormones
- Thyroid Function
- Glucose Metabolism
- Bone Marker
- Others
-
Heterophilic Blocking Reagent
- Animal Diagnostics