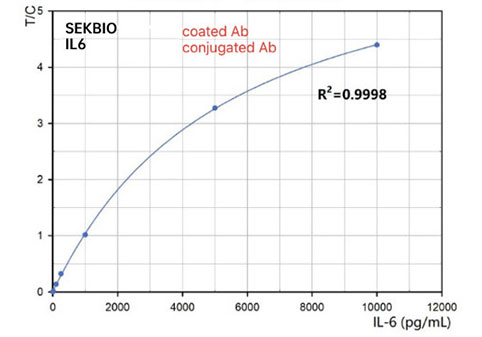
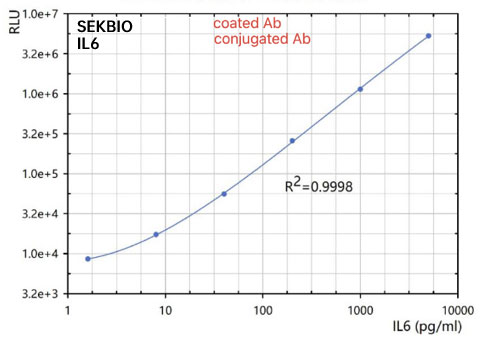
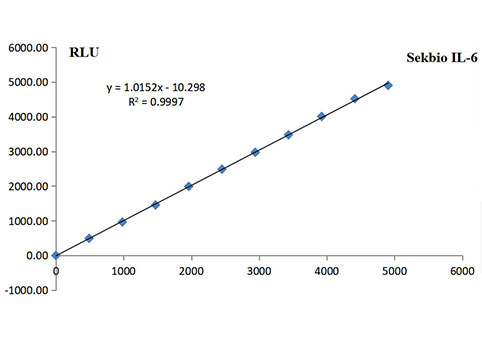
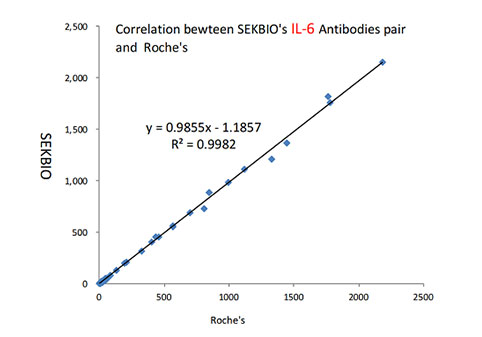
Interleukin 6 (IL6)
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine. In humans, the IL6 gene-encoded it. In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation.
Il-6 increases significantly in a variety of diseases, and its misregulated expression can cause many symptoms. It is Il-6 rapidly produced during acute inflammatory responses to internal and external injuries, surgery, stress reactions, infections, brain death, tumor formation, and other conditions.
Il-6 concentration in patients undergoing surgery can predict the risk of surgical complications.
Continuous testing of serum or plasma levels of IL-6 can effectively assess the severity of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), sepsis, and prognosis of septic shock.
Increased serum levels of IL-6 predate PCT and CRP and can use as an early warning indicator of sepsis. Il-6 also plays an essential role in chronic inflammatory responses such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Interleukin 6 (IL6) Products
| Antibody: | Catalog No. | Clone | Source | Isotype | Application |
| Mouse Anti-human IL-6 mAb | IL6-1 | Cell line uesd for fusion,CHO | Mouse IgG1 | CLIA | |
| Mouse Anti-human IL-6 mAb | IL6-2 | Cultured in vitro under conditions free from animal-derived components | Mouse IgG1 | CLIA | |
| Mouse Anti-human IL-6 mAb | IL6-Ab-01 | 1C9M | Affinity purified from cell culture supernatant | Mouse IgG1 | ELISA |
| Mouse Anti-human IL-6 mAb | IL6-Ab-02 | 1C2M | Affinity purified from cell culture supernatant | Mouse IgG1 | ELISA |
| Mouse Anti-human IL-6 mAb | IL6-Ab-03 | 3E5M | Affinity purified from cell culture supernatant | Mouse IgG1 | LFA |
| Mouse Anti-human IL-6 mAb | IL6-Ab-04 | 7C1M | Affinity purified from cell culture supernatant | Mouse IgG1 | LFA |
| Antigen: | Catalog No. | Clone | Source | Isotype | Application |
| IL6-Ag | E. coli |
Interleukin 6 Protein
Interleukin-6 is a cytokine in the chemokine family. In 1980, fibroblasts stimulated by Poly I-C can produce a cytokine that inhibits virus replication, called interferon β2 (IFN-β2). Subsequent research results failed to confirm the direct antiviral effect of this factor, but it has many other biological functions. According to the different experimental systems and functions, they were named as hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor (HPGF), B cell differentiation factor (BCDF), B cell-stimulating factor-2 ( b cell stimulatory factor 2, BSF-2), 26kDa, cytolytic T cell differentiation factor (CDF) and hepatocyte stimulating factor (HSF), etc. In 1986, the unified name of interleukin 6 (interleukin 6, IL-6).
Interleukin 6 Antibody
The primary function of interleukin-6
(1) Stimulate the proliferation of activated B cells and secrete antibodies;
(2) Stimulate T cell proliferation and CTL activation;
(3) Stimulate hepatocytes to synthesize acute phase proteins and participate in inflammatory responses;
(4) Promote blood cell development;
(5) Promote osteogenic differentiation and calcium-forming ability of human aortic valve interstitial cells.