Syphilis TP
Syphilis is a chronic sexually transmitted disease caused by infection with the spirochete Treponema pallidum (T. pallidum). It can be transmitted via blood, sexual contact, and from mother to child. After infecting mucous membranes of the genital system, T. pallidum can spread to other organs via the bloodstream and lymphatic system, resulting in chronic damage or even failure of multiple organs. Late-stage syphilis is usually accompanied by severe cardiovascular and neurological diseases. In pregnant women, syphilis can lead to premature delivery, stillbirth, and fetal malformation. According to the World Health Organization, there are around 10 million new cases of syphilis infection each year worldwide, mainly distributed in countries such as Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America. Currently, antibiotic therapy, primarily with penicillin, is the main treatment for syphilis. Due to the often indistinct early symptoms of syphilis, lack of prompt and effective treatment can ultimately lead to severe late-stage syphilis.Currently, serological methods based on recombinant Tp antigens have demonstrated significant advantages in syphilis serological diagnosis due to their high specificity, sensitivity, reproducibility.
Syphilis is a chronic sexually transmitted disease caused by Treponema pallidum (T. pallidum) infection, which can be spread through blood, sexual contact, and mother-to-child transmission. After infecting the genital mucosa, T. pallidum can disseminate throughout the body via the bloodstream and lymphatic system, leading to chronic organ damage and even failure. Late-stage syphilis often presents with severe cardiovascular and neurological disease. Pregnant women with syphilis are at risk of premature birth, stillbirth, and fetal malformation. According to the World Health Organization, there are an estimated 10 million new cases of syphilis worldwide each year, mainly in countries such as Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America. Currently, antibiotic treatment using primarily penicillin is the mainstay treatment for syphilis. Early diagnosis and treatment of syphilis are necessary to prevent late-stage disease, as early symptoms of syphilis are often not obvious.
Treponema pallidum Antigen - recombinant Antigen product
The recombinant TP antigen in this product is a fusion antigen (TP15-17-47) based on the molecular weights of 15 kDa (TP15), 17 kDa (TP17), and 47 kDa (TP47) of membrane lipoproteins from Treponema pallidum. Research has demonstrated that the three proteins, Tp15 (Tp0171), Tp17 (Tp0435), and Tp47 (Tp0574), exhibit robust expression throughout various stages of syphilis, they can induce strong inflammatory responses and immune reactions in humans.
The TP genome has a total length of 1,138,006 bp and contains 1,041 open reading frames, with twelve membrane protein families and some hemolysins considered as virulence factors. Membrane proteins are the major antigenic proteins of TP, which can induce a strong immune response in the host. Current research suggests that inflammation caused by TP lipoproteins is the main reason for immune damage in the host. The most widely used recombinant antigens for diagnosis include Tp membrane lipoproteins, such as Tp15 (Tp0171), Tp17 (Tp0435), Tp47 (Tp0574), and Tp44.5 (Tp0768). Using recombinant proteins as diagnostic antigens can achieve specificity and sensitivity of 95%-99% for syphilis diagnosis.
This product is based on a recombinant fusion antigen TP15-17-47, which consists of three antigens with molecular weights of 15kDa (Tp15), 17kDa (Tp17), and 47kDa (Tp47).
TP17 accounts for approximately 2% of TP soluble proteins and plays an important role in the early stage of infection. TP15 can interact with human host proteins, helping to maintain the survival of the microbe in the host. TP47 has strong immunogenicity and is abundant in TP, playing an important role in forming and maintaining the cell membrane of the pathogen. It can also disrupt tight junctions of endothelial cells and promote the release of the pathogen. Tp47 and Tp15 are strongly expressed in different stages of syphilis. All three proteins can stimulate inflammatory responses and immune reactions in the host immune system. Studies suggest that Tp47, Tp15, and Tp17 can activate NFκB and induce macrophages to produce inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, and IL-8 through the TLR2 receptor pathway.
Source | Escherichia Coli |
Isoelectric point | 6.29 |
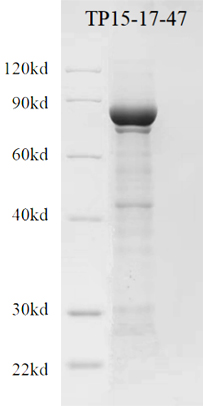
Molecular weight | 66.36kDa,theoretically |
FORMAT | Purified, liquid |
PURITY | ≥90% (SDS-PAGE) |
Figure 2: Electrophoresis of recombinant TP15-17-47
Performance
The performance of the product, on both the ELISA and LFA platform, the results of testing the China National serologic Reference Panel are as follows:
Negative control Number | ELISA Result | LFA Result | Positive Control Number | ELISA Result | LFA Result |
N1 | 0.006 | Negative | P1 | 2.201 | Positive |
N2 | 0.005 | Negative | P2 | 0.386 | Positive |
N3 | 0.005 | Negative | P3 | 2.831 | Positive |
N4 | 0.006 | Negative | P4 | 1.127 | Positive |
N5 | 0.003 | Negative | P5 | 2.688 | Positive |
N6 | 0.005 | Negative | P6 | 0.511 | Positive |
N7 | 0.078 | Negative | P7 | 1.602 | Positive |
N8 | 0.001 | Negative | P8 | 0.827 | Positive |
N9 | 0.005 | Negative | P9 | 0.347 | Positive |
N10 | 0.004 | Negative | P10 | 2.654 | Positive |
N11 | 0.006 | Negative | |||
N12 | 0.007 | Negative | |||
N13 | 0.006 | Negative | |||
N14 | 0.007 | Negative | Sensitivity Control | ||
N15 | 0.003 | Negative | Number | ELISA Result | LFA Result |
N16 | 0.004 | Negative | L1 | 1.461 | Positive |
N17 | 0.005 | Negative | L2 | 0.641 | Positive |
N18 | 0.006 | Negative | L3 | 0.289 | Positive |
N19 | 0.011 | Negative | L4 | 0.006 | Negative |
N20 | 0.008 | Negative |
The test result based on SEKBIO syphilis recombinant antigens is consistent with the reference result.
LFA Master sheet
Test Principle
The Syphilis Rapid Test Device (Whole Blood/Serum/Plasma) is a membrane-based immunoassay that detects TP antibodies (IgG and IgM) qualitatively in whole blood, serum, or plasma. The test utilizes recombinant Syphilis antigen immobilized in the test line region and Syphilis antigen-coated particles in the test to interact with the specimen. A chromatographic migration process then takes place from the specimen well to the length of the test device, allowing interaction between the mixture and the immobilized Syphilis antigen. The double antigen test format enables detection of both IgG and IgM in specimens. If TP antibodies are present in the specimen, a colored line appears in the test line region, indicating a positive result. In contrast, if TP antibodies are absent, a colored line does not appear in this region, indicating a negative result. To function as a procedural control, a colored line always appears in the control line region, ensuring proper volume of specimen addition and membrane wicking.
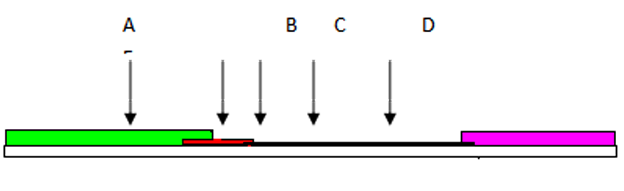
Figure 1: Test Principle
As shown in Figure 1 above, the specimen (A) migrates via capillary action along the membrane to react with the colored conjugate (B). TP antibodies present in the specimen bind to the conjugate, forming a colored antibody-antigen complex (C). TP recombinant antigen immobilized in the test zone of the membrane captures the complex. The formation of a visible red line indicates a positive result (D). The absence of a red line in the test line region indicates a negative result.
Interpretation of Results
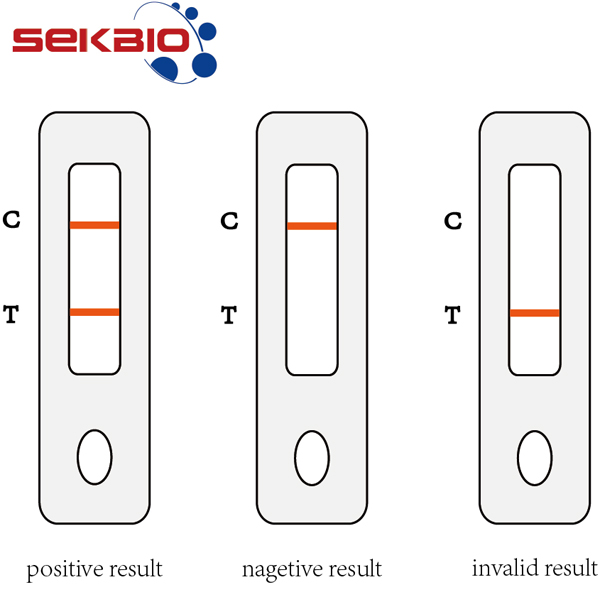
Figure 3: Interpretation of Results
Positive result:A colored band appears in the control band region (C) and another colored band appears in the T band region.
Nagetive result:One colored band appears in the control band region (C). No band appears in the test band region (T)
Invalid result:Control band fails to appear. Results from any test which has not produced a control band at the specified reading time must be discarded. Please review the procedure and repeat with a new test. If the problem persists, discontinue using the kit immediately and contact your local distributor.
Quality Control
A procedural control is included in the test.A red line appearing in the control region (C) is an internal positive procedural control. It confirms sufficient specimen volume and correct procedural technique.
Control standards are not supplied with this kit; however, it is recommended that positive and negative controls be tested as a good laboratory practice to confirm the test procedure and to verify proper test performance.


















