Luteinizing Hormone(LH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH) is a gonadotropin hormone secreted by the cells of the anterior pituitary gland. It is a glycoprotein that promotes the conversion of cholesterol into sex hormones within the gonadal cells. In females, LH works in conjunction with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) to promote follicle maturation, secretion of estrogen, ovulation, and the formation and maintenance of the corpus luteum. In males, LH stimulates the synthesis and release of testosterone by the interstitial cells of the testes.
How is LH synthesized?
LH is secreted by the alkalineophilic cells of the anterior pituitary gland. It acts on mature ovarian follicles, triggering ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum.
What are the normal values of LH?
Normal LH levels vary depending on the physiological stage in females.
For males, the normal range is between 1.5 IU/L and 9.3 IU/L.
For females:
- During the follicular phase, the normal range of LH is between 1.9 IU/L and 12.5 IU/L.
- During ovulation, the normal range of LH is between 8.7 IU/L and 76.3 IU/L.
- During the luteal phase, the normal range of LH is between 0.5 IU/L and 16.9 IU/L.
- During menopause, the normal range of LH is between 15.9 IU/L and 54 IU/L.
- During pregnancy, the normal range of LH is between 0 IU/L and 1.5 IU/L.
Both high and low LH levels in females can affect estrogen secretion, leading to abnormal ovulation and potentially impacting fertility.
Clinical applications of LH:
- Ovulation testing and assessment of gonadal function in females:
LH primarily acts on the ovaries, and its concentration can impact the maturation and development of follicles. Changes in LH levels can affect the synthesis and secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), leading to the appearance of non-dominant follicles and mature follicles. This ultimately affects female ovulation, resulting in infertility and menstrual irregularities.
- Assessment of gonadal function in males:
In males, LH acts on the testes, stimulating the secretion of testosterone by the interstitial cells and promoting the development of the germinal epithelium and sperm production. LH levels in the serum can vary due to dysfunction in any part of the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis, which regulates gonadal function. Therefore, LH is an important indicator for evaluating male gonadal function.
The performance data of the LH rapid Quantitative Test Kit (FIA)
Manufacturer | SEKBIO |
Parameter | LH Rapid Quantitative Test Kit (FIA) |
Linearity | 1~100mIU/ml |
Detection limit | 1mIU/ml |
Benchmark product | Roche |
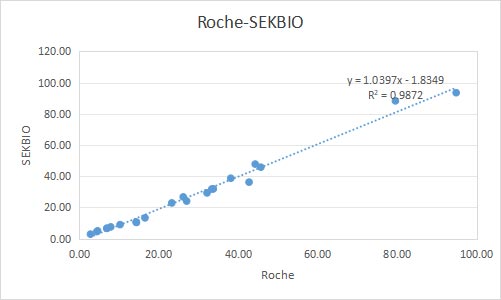
Linearity
4 Precision
Cal | Conc. mIU/ml | Cal | Conc. mIU/ml | Cal | Conc. mIU/ml |
R1 | 3.79 | R2 | 9.26 | R3 | 22.99 |
3.62 | 10.41 | 23.00 | |||
3.33 | 9.84 | 22.83 | |||
3.07 | 11.07 | 22.69 | |||
3.86 | 10.09 | 24.37 | |||
3.63 | 11.11 | 28.38 | |||
2.95 | 11.28 | 29.52 | |||
3.84 | 11.79 | 25.89 | |||
3.45 | 11.72 | 23.66 | |||
2.97 | 9.15 | 28.32 | |||
AVE | 3.45 | AVE | 10.57 | AVE | 25.16 |
SD | 0.35 | SD | 0.96 | SD | 2.66 |
CV | 10.3% | CV | 9.1% | CV | 10.6% |
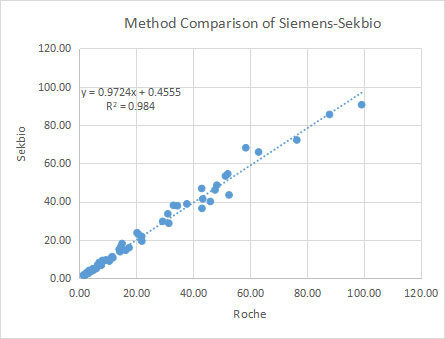
5 Method Comparison
The performance data of the LH Rapid Quantitative Test Kit(CLIA)
Sensitivity
Sample Concentration (mIU/mL) | RLU | Average | CV | S/N | |
219.85 | 3,101,159 | 3,280,048 | 3,190,604 | 3.96% | 7169.9 |
188.08 | 2,780,782 | 2,679,790 | 2,730,286 | 2.62% | 6135.5 |
78.25 | 957,837 | 924,700 | 941,269 | 2.49% | 2115.2 |
17.68 | 107,259 | 112,512 | 109,886 | 3.38% | 246.9 |
4.03 | 12,231 | 12,125 | 12,178 | 0.62% | 27.4 |
0.14 | 422 | 468 | 445 | 7.31% | 1.0 |
Precision
Control (mIU/mL) | RLU | Concentration | Control (mIU/mL) | RLU | Concentration |
4.03 | 11,406 | 3.85 | 78.25 | 975,722 | 80.37 |
12,213 | 4.04 | 939,999 | 78.18 | ||
11,134 | 3.79 | 924,754 | 77.24 | ||
10,887 | 3.73 | 943,991 | 78.43 | ||
10,502 | 3.64 | 949,239 | 78.75 | ||
11,261 | 3.82 | 946,420 | 78.57 | ||
11,311 | 3.83 | 997,573 | 81.71 | ||
12,311 | 4.06 | 967,323 | 79.86 | ||
10,525 | 3.65 | 933,076 | 77.75 | ||
10,416 | 3.62 | 956,326 | 79.18 | ||
AVE | 2,353 | 77.66 | AVE | 671,260 | 4923.57 |
SD | 664.89 | 0.15 | SD | 21653.14 | 1.33 |
CV | 4.78% | 2.43% | CV | 2.05% | 1.94% |
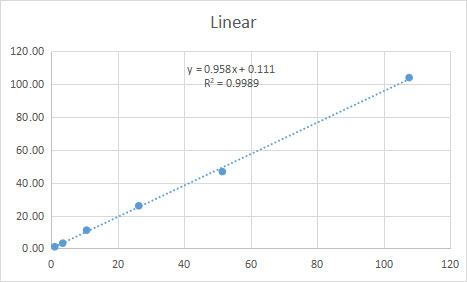
Linear
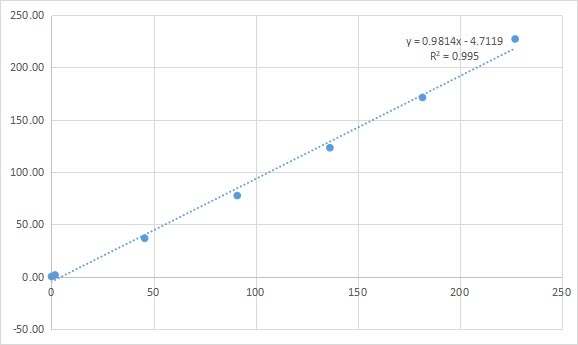
Method Comparison