HCV
HCV hepatitis C virus
Recombinant Antigens and master sheet product
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) belongs to the family of hepatotropic viruses, and infection with this virus can lead to liver damage. It is the main cause of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Epidemiological studies have shown that global HCV infection rates exceed 185 million, with only 15% to 25% of infected individuals able to clear the virus through their immune response. The remaining 75% to 85% of infected individuals will develop chronic hepatitis C (CHC). Among CHC patients, 15% to 30% will develop cirrhosis, ultimately leading to liver cancer. In addition, HCV infection can result in various extrahepatic manifestations, most commonly diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and depression.
HCV belongs to the Flaviviridae family, with a genome consisting of a single positive-strand RNA of 9.7 nt in length, containing a 5' UTR and an open reading frame with a 3' UTR. The open reading frame encodes for a large precursor protein that is cleaved by protease into structural proteins, mainly consisting of core and envelope proteins (E1, E2), and non-structural proteins including p7, NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B.
Due to the lack of proofreading function in the key enzyme for virus proliferation, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), the HCV viral genome exhibits a high degree of variability. HCV strains can be divided into 8 genotypes and nearly 100 subtypes.Due to the genetic diversity of the hepatitis C virus, there is still a lack of effective vaccines for hepatitis C.In the treatment of HCV, the Peg-IFN and ribavirin combination therapy (PR regimen) was once the mainstay treatment for CHC. However, due to its limited efficacy and significant side effects, it has gradually been replaced by various types of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) regimens developed subsequently. These drugs include non-structural proteins 3/4A protease inhibitors, NS5A inhibitors, NS5B polymerase nucleotide analogue inhibitors, and potent CYP3A4 inhibitors. By using two or more of these drugs in combination.
Despite the development of highly effective drugs with a high cure rate, the majority of patients with HCV infection remain untreated. Due to the ease of chronicization, the lack of overt clinical symptoms in early HCV infection, and the general lack of HCV screening, only about 20% of hepatitis C patients are diagnosed. Therefore, early screening for hepatitis C is particularly important. Clinical laboratory techniques include ELISA, GICA, CMIA, ECLIA, and fluorescent qPCR. The flexible combination of these detection techniques can minimize misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis during the optimal window period. HCV-RNA and HCV-cAg detection are important indicators currently used clinically to diagnose hepatitis C.
Performance evaluation based on HCV recombinant antigen
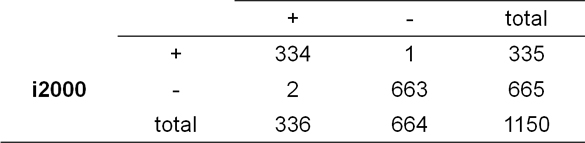
A. On the chemiluminescent immunoassay platform, there is a high correlation with the results from Abbott's result.
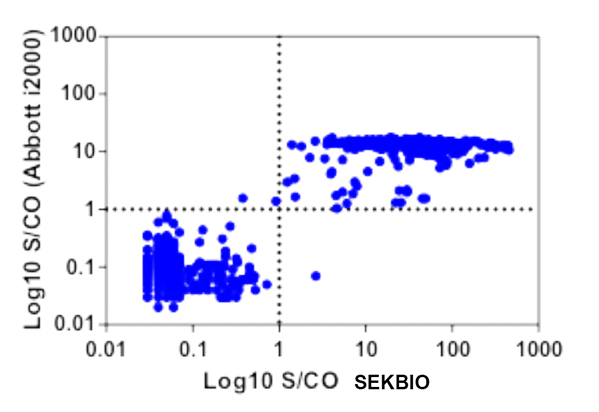
SEKBIO
B. On the ELISA platform, the evaluation result of our product on Chinese HCV National serologic reference panel is as follows (indirect method)
Sample No. | ELISA | LFA Result | Sample No. | ELISA | LFA Result | Sample No. | ELISA Result | LFA Result |
N1 | 0.007 | Negative | P1 | 2.780 | Positive | L1 | 0.805 | Positive |
N2 | 0.005 | Negative | P2 | 3.199 | Positive | L2 | 0.368 | positive |
N3 | 0.009 | Negative | P3 | 2.951 | Positive | L3 | 0.322 | Positive |
N4 | 0.007 | Negative | P4 | 0.323 | Positive | L4 | / | Negative |
N5 | 0.008 | Negative | P5 | 3.090 | Positive | |||
N6 | 0.005 | Negative | P6 | 2.997 | Positive | |||
N7 | 0.007 | Negative | P7 | 2.578 | Positive | |||
N8 | 0.008 | Negative | P8 | 3.199 | Positive | |||
N9 | 0.006 | Negative | P9 | 1.480 | Positive | |||
N10 | 0.033 | Negative | P10 | 3.154 | Positive | |||
N11 | 0.009 | Negative | P11 | 2.966 | Positive | |||
N12 | 0.006 | Negative | P12 | 2.980 | Positive | |||
N13 | 0.005 | Negative | P13 | 2.938 | Positive | |||
N14 | 0.006 | Negative | P14 | 2.913 | Positive | |||
N15 | 0.007 | Negative | P15 | 2.872 | Positive | |||
N16 | 0.004 | Negative | P16 | 3.115 | Positive | |||
N17 | 0.007 | Negative | P17 | 2.953 | Positive | |||
N18 | 0.348 | Negative | P18 | 3.201 | Positive | |||
N19 | 0.007 | Negative | P19 | 3.007 | Positive | |||
N20 | 0.005 | Negative | P20 | 0.980 | Positive | |||
N21 | 0.004 | Negative | P21 | 2.853 | Positive | |||
N22 | 0.005 | Negative | P22 | 0.944 | Positive | |||
N23 | 0.005 | Negative | P23 | 1.842 | Positive | |||
N24 | 0.000 | Negative | P24 | 0.748 | Positive | |||
N25 | 0.006 | Negative | P25 | 2.827 | Positive | |||
N26 | 0.007 | Negative | P26 | 3.252 | Positive | |||
N27 | 0.007 | Negative | P27 | 0.481 | Positive | |||
N28 | 0.006 | Negative | P28 | 0.538 | Positive | |||
N29 | 0.042 | Negative | P29 | 0.130 | P/N | |||
N30 | 0.006 | Negative | P30 | 0.928 | Positive |
C. On the ELISA platform, the results of the CHIINA National Serologic Reference Panel are as follows (sandwich method)
Sample No. | Result | Sample No. | Result | Sample No. | Result |
N1 | 0.004 | P1 | 2.906 | L1 | 1.250 |
N2 | 0.001 | P2 | 0.904 | L2 | 1.279 |
N3 | 0.004 | P3 | 0.947 | L3 | 1.441 |
N4 | 0.003 | P4 | 0.913 | L4 | 0.06 |
N5 | 0.001 | P5 | 2.984 | CV | 1.363 |
N6 | 0.001 | P6 | 2.827 | ||
N7 | 0.001 | P7 | 0.974 | ||
N8 | 0.001 | P8 | 3.022 | ||
N9 | 0.004 | P9 | 2.970 | ||
N10 | 0.001 | P10 | 2.933 | ||
N11 | 0.004 | P11 | 2.931 | ||
N12 | 0.001 | P12 | 0.648 | ||
N13 | 0.030 | P13 | 2.904 | ||
N14 | 0.002 | P14 | 2.949 | ||
N15 | 0.002 | P15 | 2.945 | ||
N16 | 0.002 | P16 | 2.976 | ||
N17 | 0.003 | P17 | 2.863 | ||
N18 | 0.472 | P18 | 2.931 | ||
N19 | 0.004 | P19 | 2.886 | ||
N20 | 0.002 | P20 | 2.503 | ||
N21 | 0.005 | P21 | 2.891 | ||
N22 | 0.003 | P22 | 2.828 | ||
N23 | 0.003 | P23 | 2.973 | ||
N24 | 0.003 | P24 | 2.745 | ||
N25 | 0.007 | P25 | 2.460 | ||
N26 | 0.005 | P26 | 2.866 | ||
N27 | 0.003 | P27 | 0.952 | ||
N28 | 0.004 | P28 | 0.760 | ||
N29 | 0.004 | P29 | 0.243 | ||
N30 | 0.005 | P30 | 0.432 |


















