INS(Insulin)
Introduction:
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas, and it plays a crucial role in regulating glucose (sugar) metabolism in the body. The primary function of insulin is to facilitate the uptake of glucose by cells, where it can be used for energy. Insulin helps maintain optimal blood sugar levels by promoting the storage of excess glucose in the liver and muscles, preventing it from accumulating in the bloodstream.
In the realm of diabetes management and metabolic health, insulin plays a pivotal role in regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin tests are essential diagnostic tools that provide valuable insights into an individual's insulin production and help in assessing overall metabolic health. In this article, we will delve into the significance of insulin tests, their purpose, and what the results may indicate.
Clinical Significance of Insulin Test:
1. Diagnosis of Diabetes
2. Monitoring Diabetes Treatment
3. Assessment of Insulin Resistance
4. Evaluation of Pancreatic Function
5. Hypoglycemia Investigations
6. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Diagnosis
The performance data of the INS Rapid Quantitative Test Kit(CLIA)
Manufacturer | SEKBIO |
Parameter | INS |
Linearity | 0.2-1000uIU/mL |
Detection limit | 0.01uIU/mL |
Six point calibration test results
Sample Concentration ( uIU/ml) | RLU | Average | CV | S/N | ||
1,014.31 | 1,172,979 | 1,050,097 | 1,151,211 | 1,124,762 | 5.83% | 962.43 |
200.09 | 204,519 | 236,269 | 200,489 | 213,759 | 9.17% | 182.91 |
20.85 | 20,916 | 21,322 | 23,821 | 22,020 | 7.14% | 18.84 |
1.95 | 3,033 | 2,775 | 3,191 | 3,000 | 7.00% | 2.57 |
0.22 | 1,485 | 1,460 | 1,402 | 1,449 | 2.94% | 1.24 |
0.02 | 1,124 | 1,158 | 1,224 | 1,169 | 4.35% | 1.00 |
Precision
Sample | RLU | Concentration | Sample | RLU | Concentration |
0.25 | 3,048 | 2.00 | 15.21 | 196,412 | 184.18 |
3,002 | 1.96 | 216,766 | 202.86 | ||
3,076 | 2.03 | 221,674 | 207.36 | ||
3,191 | 2.15 | 225,286 | 210.67 | ||
3,057 | 1.98 | 206,126 | 193.10 | ||
3,053 | 2.01 | 195,386 | 183.24 | ||
3,245 | 2.21 | 190,951 | 179.16 | ||
3,269 | 2.24 | 226,027 | 211.35 | ||
3,064 | 2.02 | 226,762 | 212.02 | ||
3,409 | 2.38 | 210,788 | 197.38 | ||
AVE | 3,141 | 2.10 | AVE | 211,618 | 198.13 |
SD | 131.00 | 0.14 | SD | 13760.15 | 12.63 |
CV | 4.17% | 6.67% | CV | 6.50% | 6.37% |
Limit of detection
Sample | RLU | Concentration | ||
Ag Diluent | 1,222 | 1,206 | 0.07 | 0.06 |
1,231 | 1,267 | 0.08 | 0.09 | |
1,273 | 1,117 | 0.13 | 0.03 | |
1,270 | 1,171 | 0.09 | 0.03 | |
1,110 | 1,134 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
1,141 | 1,331 | 0.03 | 0.19 | |
1,161 | 1,176 | 0.00 | 0.04 | |
1,223 | 1,279 | 0.07 | 0.13 | |
1,129 | 1,123 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
1,171 | 1,262 | 0.04 | 0.14 | |
AVE | 1,200 | 0.07 | ||
SD | 65.51 | 0.05 | ||
AVE+2*SD | 0.164 | |||
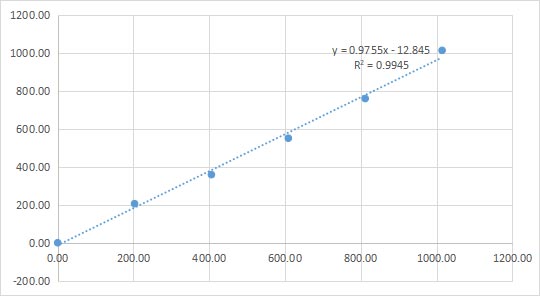
Linear
Sample(uIU/ml) | Dilution ratio | Concentration value | Average | ||
1014.31 | 1.0 | 1056.80 | 948.51 | 1037.63 | 1014.31 |
811.49 | 0.8 | 767.04 | 753.74 | 760.49 | 760.42 |
608.67 | 0.6 | 552.77 | 518.70 | 582.22 | 551.23 |
405.86 | 0.4 | 342.35 | 381.00 | 354.64 | 359.33 |
203.04 | 0.2 | 224.90 | 194.47 | 199.70 | 206.36 |
0.22 | 0.0 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.22 |
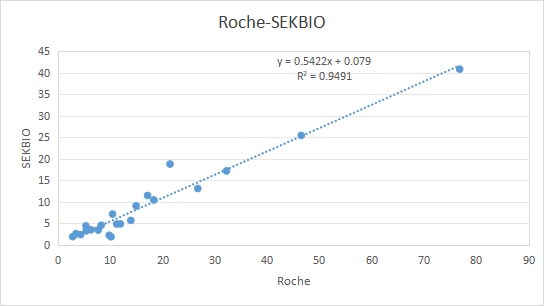
Method Comparison

- Cardiac Markers
-
Tumor Marker
-
PGII
-
G17
- CA50
-
CA125
- CA242
-
CA15-3
- CA19-9
- CA72-4
-
Pepsinogens I (PGI)
-
Human Epididymis 4 (HE4)
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
- Neuron-Specific Enolase (NSE)
- Cytokeratin 19 Fragment (CYFRA21-1)
- Human Progastrin-releasing Peptide (ProGRP Tumor Marker)
- Protein Induced by Vitamin K Absence or Antagonist-II (PIVKA II Tumor Marker)
- Alpha-fetoprotein(AFP)
-
CEA
-
Human Chitinase 3-like 1
-
PGII
- Inflammatory Marker
- Infectious Disease
- Hormones
- Thyroid Function
- Glucose Metabolism
- Bone Marker
- Others
-
Heterophilic Blocking Reagent
- Animal Diagnostics

















