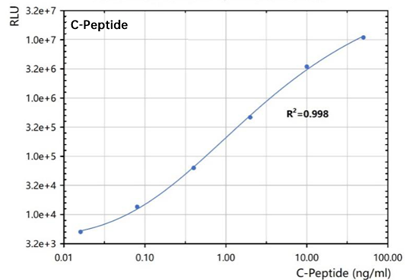
C-Peptide
The connecting peptide, or C-peptide, is a short 31-amino-acid polypeptide that connects insulin's A-chain to its B-chain in the proinsulin molecule, releasing C-peptide and insulin from the pancreas at the same time and in about equal amounts.
So a C-peptide test can show how much insulin your body is making.
This test can be an excellent way to measure insulin levels because C-peptide tends to stay in the body longer than insulin.
A C-peptide test can help tell the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. With type 1 diabetes, your pancreas makes little to no insulin and little or no C-peptide. With type 2 diabetes, the body produces insulin but doesn't use it well, which can cause C-peptide levels to be higher than usual.
The performance data of the C-P Rapid Quantitative Test Kit(CLIA)
Manufacturer | SEKBIO |
Parameter | C-P |
Linearity | 0.01-40 ng/ml |
Detection limit | 0.01 ng/ml |
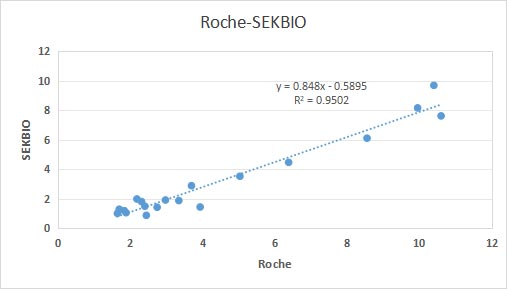
benchmark product | Roche |
Test principle and procedure | C-P: Add 15 μl of sample + 30 μl of Rd+30 μl of Raincubation for 15 minutes. Wash with 200 μl of washing solution. Finally, add 100 μl of A + 100 μl of B. |
Six point calibration test results
Sample Concentration( ng/ml ) | RLU | Average | CV | S/N | ||
39.09 | 2,868,141 | 2,984,878 | 2,920,778 | 2,924,599 | 2.00% | 3851.54 |
20.61 | 1,635,030 | 1,709,528 | 1,595,685 | 1,646,748 | 3.51% | 2168.68 |
5.14 | 335,216 | 337,270 | 351,423 | 341,303 | 2.59% | 449.48 |
0.47 | 17,622 | 17,873 | 17,701 | 17,732 | 0.72% | 23.35 |
0.04 | 1,511 | 1,473 | 1,566 | 1,517 | 3.08% | 2.00 |
0.00 | 764 | 755 | 759 | 759 | 0.59% | 1.00 |
Precision
Sample | RLU | Concentration | Sample | RLU | Concentration |
0.5 | 18,399 | 0.49 | 20 | 1,680,161 | 21.03 |
17,298 | 0.46 | 1,646,289 | 20.60 | ||
17,366 | 0.47 | 1,624,950 | 20.34 | ||
18,393 | 0.49 | 1,636,695 | 20.48 | ||
17,898 | 0.48 | 1,683,839 | 21.08 | ||
18,312 | 0.49 | 1,686,358 | 21.11 | ||
18,445 | 0.49 | 1,693,393 | 21.20 | ||
18,105 | 0.48 | 1,668,111 | 20.88 | ||
18,566 | 0.49 | 1,698,111 | 21.26 | ||
18,330 | 0.49 | 1,687,107 | 21.12 | ||
AVE | 18111.20 | 0.48 | AVE | 1,670,501 | 20.91 |
SD | 451.02 | 0.01 | SD | 25591.77 | 0.32 |
CV | 2.49% | 2.08% | CV | 1.53% | 1.54% |
Limit of detection
Sample | RLU | Concentration | ||
Ag Diluent | 814 | 825 | 0 | 0 |
945 | 817 | 0.006 | 0 | |
743 | 783 | 0 | 0 | |
805 | 822 | 0 | 0 | |
779 | 835 | 0 | 0 | |
804 | 555 | 0 | 0 | |
791 | 855 | 0 | 0 | |
701 | 791 | 0 | 0 | |
827 | 605 | 0 | 0 | |
831 | 770 | 0 | 0 | |
AVE | 784.90 | 0.00 | ||
SD | 84.89 | 0.00 | ||
AVE+2*SD | 0.003 | |||
Linear
Sample(ng/ml) | Dilution ratio | Concentration value | Average | ||
38.89 | 1.0 | 39.204 | 39.22 | 38.251 | 38.89 |
31.12 | 0.8 | 33.451 | 33.539 | 33.717 | 33.57 |
23.35 | 0.6 | 26.043 | 25.641 | 26.05 | 25.91 |
15.58 | 0.4 | 17.691 | 18.047 | 18.199 | 17.98 |
7.81 | 0.2 | 9.627 | 9.899 | 9.804 | 9.78 |
0.04 | 0.0 | 0.041 | 0.04 | 0.044 | 0.04 |
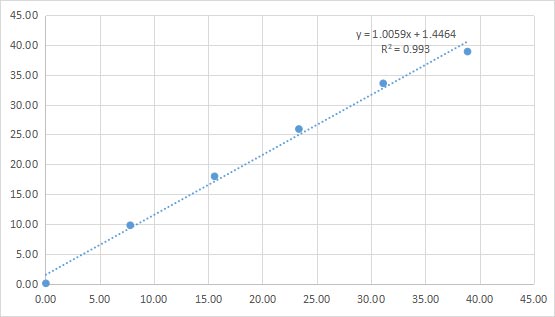
Method Comparison
Reagents Stability
Reagent | Sample( ng/ml) | Average | Deviation |
2-8° | 40.00 | 2,673,041 | |
5.00 | 305,357 | ||
0.50 | 16,436 | ||
0.00 | 683 | ||
37℃ 1d | 40.00 | 2,524,613 | -5.55% |
5.00 | 286,392 | -6.21% | |
0.50 | 14,671 | -10.74% | |
0.00 | 509 | -25.55% | |
37℃ 4d | 40.00 | 2,413,430 | -9.71% |
5.00 | 287,230 | -5.94% | |
0.50 | 14,213 | -13.53% | |
0.00 | 351 | -48.68% | |
37℃ 7d | 40.00 | 2,338,396 | -12.52% |
5.00 | 272,902 | -10.63% | |
0.50 | 13,926 | -15.27% | |
0.00 | 306 | -55.20% |
Calibrator Stability
Reagent | Sample(ng/ml) | Average | Deviation |
2-8℃ | 20.00 | 3,979,931 | |
0.20 | 19,627 | ||
37℃ 1d | 20.00 | 4,009,219 | 0.74% |
0.20 | 19,241 | -1.97% | |
37℃ 4d | 20.00 | 4,094,036 | 2.87% |
0.20 | 19,275 | -1.80% | |
37℃ 7d | 20.00 | 3,964,933 | -0.38% |
0.20 | 18,882 | -3.80% |
C-Peptide Products
| Antibody | Application |
| Mouse Anti-human C-Peptide mAb | For immunodiagnostic: ELISA, LFA, CLIA |
C-Peptide Intro
C-peptide (C-Peptide), also known as a connecting peptide, is secreted by pancreatic beta cells, and it shares a common precursor with insulin, proinsulin. Proinsulin is split into one molecule of insulin and one molecule of C-peptide, so the molar amount of C-peptide and self-insulin is the same. Because the liver does not readily degrade C-peptide, C-peptide is the measurement of insulin content, accurately reflecting the function of islet cells. Blood can be drawn during the oral glucose tolerance test to measure the serum C-peptide level 1 hour, 2 hours, and 3 hours after fasting blood glucose load. The C-peptide level of ordinary people increased to more than three times the basal level after 60 minutes of glucose intake. The level of C-peptide in type 1 diabetes is deficient, and the postprandial C-peptide rise in patients with islet dysfunction is often less than 3-fold. For patients receiving insulin therapy, the auto-islet function cannot be evaluated by measuring insulin levels in the blood. Still, auto-islet β-cell function can assess by measuring C-peptide levels.
C-Peptide Test
C-peptide can reflect the secretory function of islet β cells in the body and has guiding significance for the classification of diabetic patients and the identification of hypoglycemia.
1. Diabetes
Determination of C-peptide levels can be applied to type diabetes and to understand the function of islet β cells in diabetic patients. Patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus should detect the level of C-peptide or insulin to determine islet β-cell function at the beginning of the disease.
2. Hypoglycemia
When hypoglycemia occurs in a patient suspected of having insulinoma, measuring the blood glucose to insulin ratio can help diagnose. While hypoglycemia occurs in patients treated with exogenous insulin, determination of C-peptide can identify the cause of hypoglycemia.
3. Islet transplantation
In addition to monitoring blood glucose, C-peptide should be measured to understand the secretory function of islet β cells after transplantation.
4. Liver and kidney disease
When suffering from hepatitis or cirrhosis, the hepatic uptake of insulin decreases, and the level of insulin in the blood tends to increase. At the same time, the C-peptide is less affected by it, and the ratio of C-peptide to insulin in the blood decreases. When nephropathy occurs, the degradation of C-peptide slows down, the level of C-peptide in blood increases, and the ratio of C-peptide to insulin is significantly higher than usual.