Myoglobin (Myo)
Myoglobin (myoglobin, Mb, Myo), a kind of cardiac marker, can transport and store oxygen in muscle cells and is dispersed from the heart muscle cells into the blood circulation when the heart muscle is damaged.
Determination of serum and urine can diagnose MYO certain myopathy and heart diseases, such as acute muscle injury, critical and chronic renal failure, severe congestive heart failure, prolonged shock, neuromuscular disorders such as muscular dystrophy, muscular atrophy, dermatomyositis, and myopathy caused by various factors.
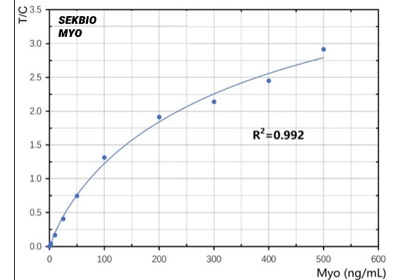
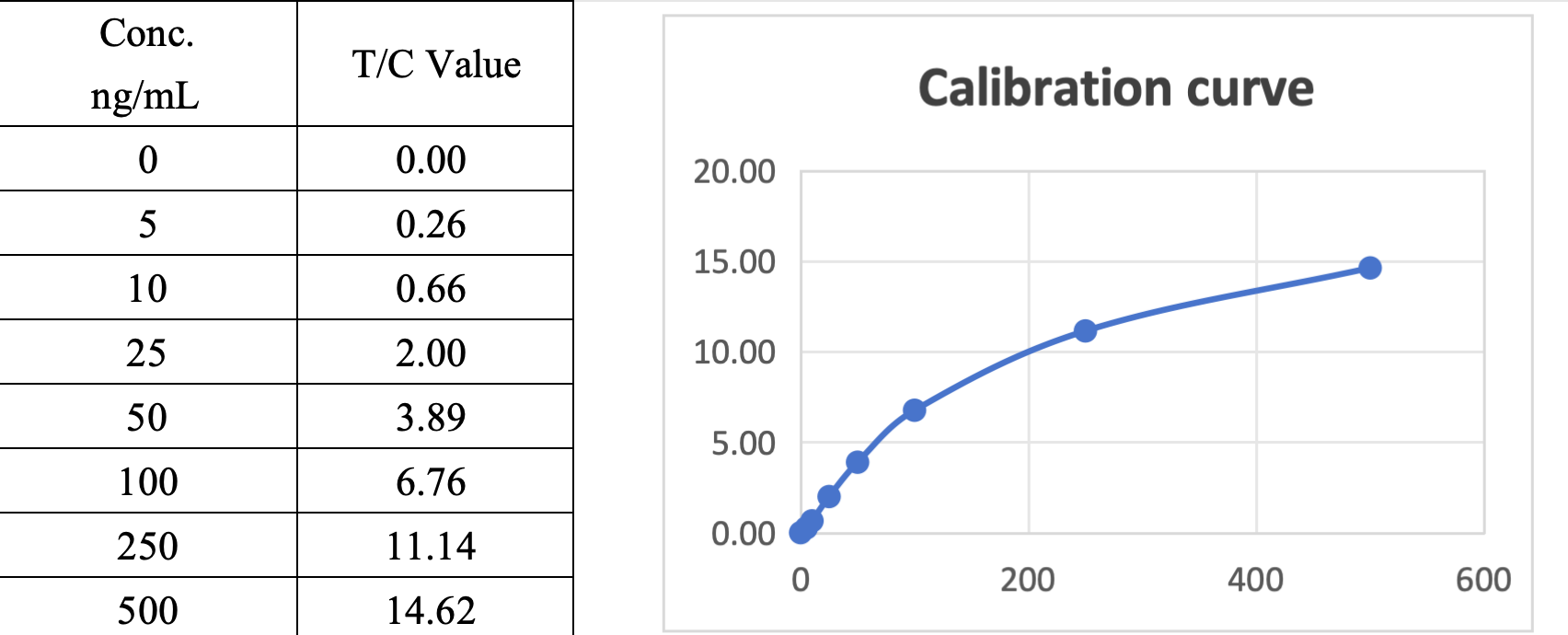
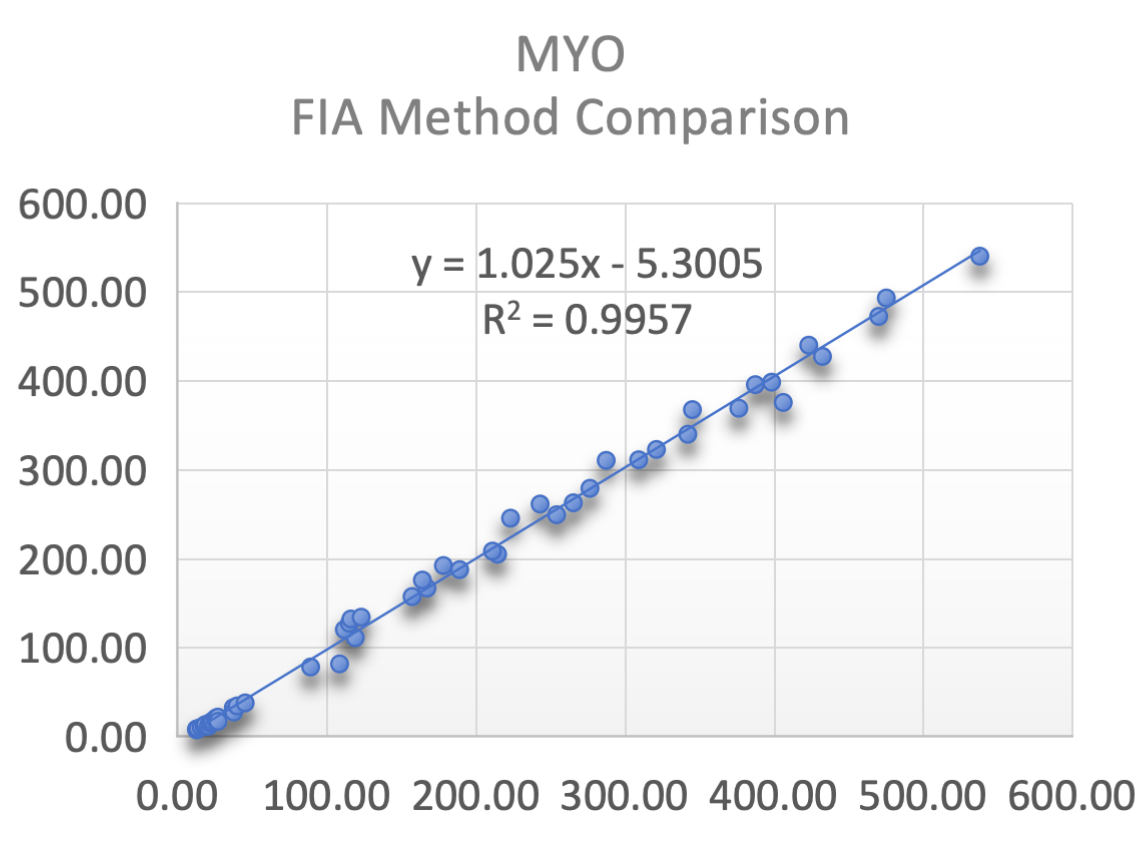
Sekbio provides Mouse Myo mAb and Recombinant Myo antigen, highly consistent with Roche's relevant products on Sekbio's CLIA platform and FIA platform.
Myoglobin (Myo) Products
| Antibody | Application |
| Mouse Myo mAb | For immunodiagnostic: ELISA, LFA, CLIA |
| Antigen | Application |
| Recombinant Myo Antigen | For immunodiagnostic: ELISA, LFA, CLIA |
Myoglobin Antibody
At present, immunological detection methods based on monoclonal antibodies are mainly used to detect myoglobin protein in clinical practice. Among them, double-antibody sandwich Elisa is suitable for the simultaneous detection of multiple samples due to its high sensitivity and specificity, and the operation is simple. It is widely used because it does not require special equipment and other advantages. In addition to high specificity and high affinity, the double-antibody sandwich Elisa antibody should also recognize different epitopes of the same antigen. The other two antibodies must also react with the natural antigen in the sample. Therefore, the quality of the prepared monoclonal antibody is the key to the successful development of the double-antibody sandwich Elisa test kit.
MYO Protein
Myoglobin (Mb) is a binding protein composed of a peptide chain and a heme prosthetic group, mainly distributed in cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue.
Serum Mb < 70ng/ml, and its level varies with age, sex, and race. Elevated serum Mb levels result from skeletal muscle or cardiomyocyte injury (lysis/necrosis) release into the blood circulation. MYO antibody can be detected in serum in the early stage after myocardial infarction, and the peak time (1-2 hours) is earlier than that of creatine kinase (CK).