Human Progastrin-releasing Peptide (ProGRP Tumor Marker)
ProGRP tumor marker is a recently identified biomarker of small cell lung cancer (SCLC). ProGRP tumor marker is a precursor of a neuropeptide hormone called a gastrin-releasing peptide (GRP), and SCLC cells frequently produce it.
Circulating proGRP levels serve as a reliable marker in patients with SCLC and are the most sensitive marker for discriminating SCLC 16 from benign lung diseases.
ProGRP marker is rarely elevating in patients with other malignancies or mild conditions except in patients with renal insufficiency, neuroendocrine tumors of the lung, and medullary carcinoma of the thyroid.
SEKBIO is now offering Mouse anti-human ProGRP mAb, Humanized anti-human ProGRP mAb, and Recombinant human proGRP 31-98 fragment (Prokaryotic expression). You may also be interested in the tumor markers list.
Introduction
ProGRP, the precursor of Gastrin-Releasing Peptide (GRP), is widely distributed in non-gastric tissues, neural fibers, the brain, and lung neuroendocrine cells. With variations in its partial amino acids, proGRP can be categorized into three bio-macromolecules, all sharing a common C-terminal sequence (31-98) and demonstrating stable expression in the plasma. This peptide is the product encoded by the GRP gene, and studies have validated that proGRP levels effectively mirror GRP levels and gene expression.
The diagnostic significance of ProGRP is particularly prominent in the field of cancer diagnostics, where it has shown a strong association with various malignancies. Recent research has highlighted the ability of ProGRP levels to accurately reflect GRP expression and its associated gene. Notably, ProGRP emerges as a valuable biomarker for the diagnosis and treatment of diverse cancers, including small-cell lung cancer, non-small-cell lung cancer, gastrointestinal tumors, small-cell esophageal cancer, and ovarian cancer.
The measurement of ProGRP levels in plasma offers a non-invasive avenue for assessing the presence and progression of these cancers. As a result, ProGRP stands out as a pivotal diagnostic tool, holding significant implications for early detection, prognosis, and the development of targeted treatment strategies within the field of oncology. Stay updated on the latest advancements in ProGRP research, as it continues to be a promising area for enhancing cancer diagnostics and improving patient outcomes.
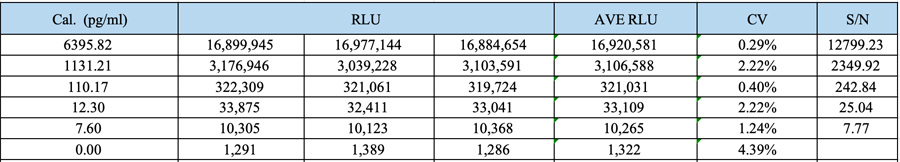
Calibration curve and its sensitivity (CLIA)
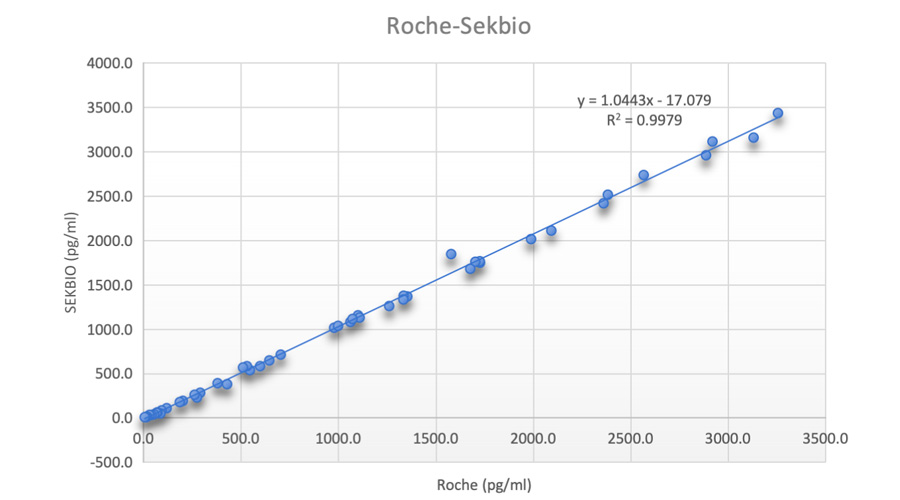
Method comparison
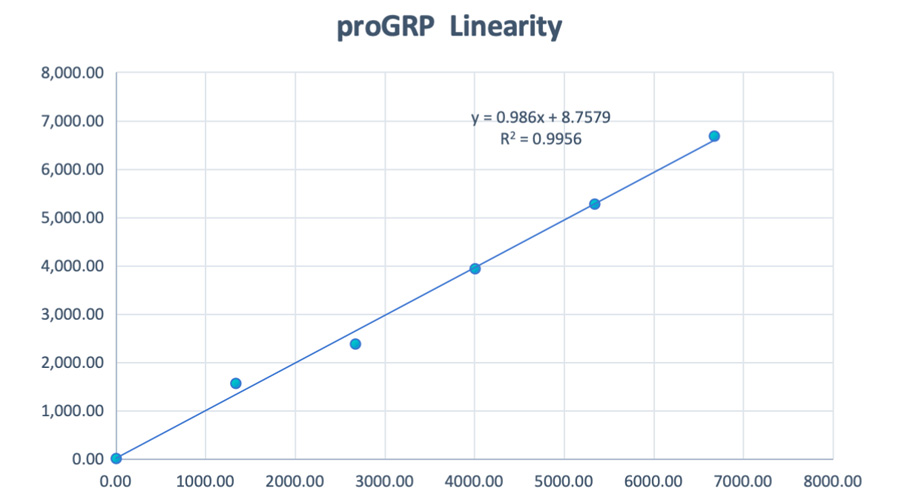
Linearity (CLIA)
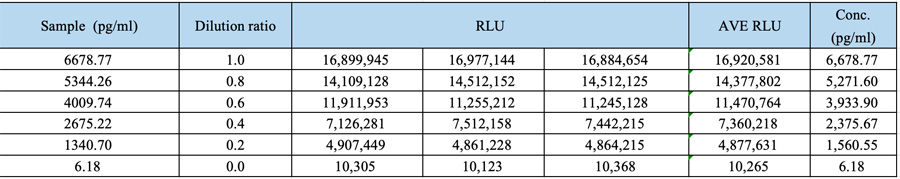
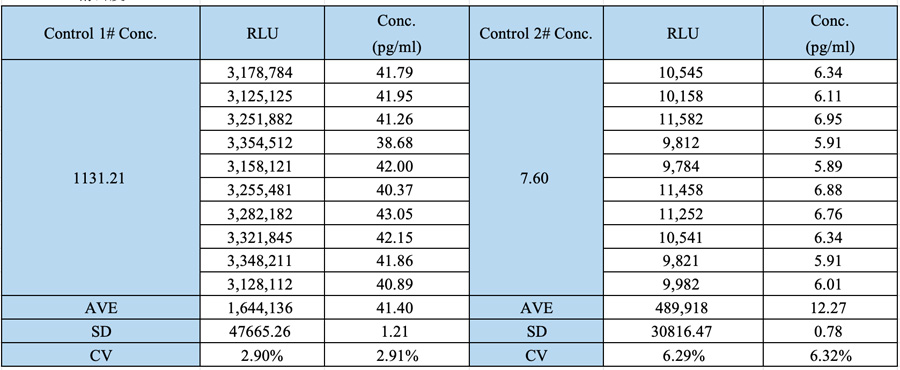
Repeatability
ProGRP Antibody Tumor Marker Products
| Antibody | Application |
| Mouse anti-human ProGRP mAb | For immunodiagnostic: ELISA, LFA, CLIA |
| Humanized anti-human ProGRP mAb |
| Antigen | Application |
| Recombinant human proGRP 31-98 fragment (Prokaryotic expression) | For immunodiagnostic: ELISA, LFA, CLIA |
ProGRP Tumor Marker Intro
The progastrin-releasing peptide is a novel small-cell lung cancer marker. PRO GRP tumor marker is a brain-gut hormone. Like a small cell lung cancer marker, PRO GRP marker has the following characteristics: 1. It has very high specificity for small cell lung cancer; 2. It has a higher positive rate in earlier cases; 3. The blood concentration of healthy people and patients is very different, so Detection reliability is increased.
ProGRP is a specific tumor marker for SCLC, which has advantages over other tumor markers in tumor specificity, release amount, and organ specificity. In addition, the concentration of ProGRP in the blood is less affected by factors such as activity and diet, with slight fluctuation during the day, and hemolysis has little effect on its test results. Therefore, ProGRP is useful for monitoring SCLC patients undergoing treatment and detecting relapse cases.
ProGRP Tumor Marker Function
The kidney is one of the main metabolic pathways of ProGRP antibody in the body, and renal insufficiency is an important reason for increasing ProGRP levels. Therefore, the influence of renal dysfunction should be excluded when ProGRP is used to assist in the diagnosis of SCLC. When the patient's creatinine concentration was >140 μmol/L, the ProGRP antibody level increased. Therefore, detecting the ProGRP concentration should check the patient's renal function at the same time to exclude the elevated ProGRP concentration caused by chronic renal disease.


















