FT3(Free Triiodothyronine)
Free Triiodothyronine (FT3) is a critical hormone in the thyroid hormone family that plays a central role in regulating metabolism in the human body. Here's a comprehensive introduction:
Overview: Free Triiodothyronine, often abbreviated as FT3, represents the biologically active fraction of the thyroid hormone T3 that is not bound to proteins in the bloodstream. It is synthesized primarily by the thyroid gland through the iodination and coupling of tyrosine residues in thyroglobulin. A smaller portion of T3 is converted from its precursor, Thyroxine (T4), in peripheral tissues such as the liver, kidney, and skeletal muscle.
Importance: FT3 is considered a more sensitive indicator of thyroid function compared to Total T3 or T4 because it reflects the hormone available to interact directly with cellular receptors. This unbound form crosses cell membranes easily and exerts its metabolic effects within cells, influencing processes like energy production, growth, and development.
Regulation and Function: The production and release of FT3 are tightly regulated by the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis. The hypothalamus secretes Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to produce and secrete Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH). TSH, in turn, prompts the thyroid gland to synthesize and release both T4 and T3. Feedback mechanisms ensure that FT3 levels remain within a narrow normal range to maintain metabolic homeostasis.
Clinical Significance: In clinical practice, measuring FT3 levels is crucial for diagnosing thyroid disorders. Elevated FT3 levels are typically seen in hyperthyroidism, a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, leading to symptoms such as weight loss, anxiety, and increased heart rate. Conversely, decreased FT3 concentrations are indicative of hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland is underactive, causing symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and depression. Moreover, FT3 levels are particularly important in assessing thyroid function in individuals with altered protein binding, as in non-thyroidal illness syndrome or during pregnancy.
Testing and Interpretation: Laboratory tests measure FT3 using techniques that isolate the free hormone from protein-bound hormones. Normal reference ranges for FT3 vary slightly depending on the laboratory method used but generally fall within approximately 3-9 pmol/L. Interpretation of results must consider factors such as age, sex, pregnancy, and individual laboratory reference intervals.
In summary, Free Triiodothyronine (FT3) is a key hormone responsible for regulating metabolism and is a fundamental parameter in evaluating thyroid gland function and diagnosing thyroid-related disorders. Its accurate measurement is essential for understanding the thyroid's impact on overall health and guiding appropriate medical interventions.
The performance data of the FT3 Rapid Quantitative Test Kit(CLIA)
Manufacturer | SEKBIO |
Parameter | FT3 |
Linearity | 0.4-50 pmol/L |
Detection limit | 0.4 pmol/L |
benchmark product | Roche |
Test principle and procedure | FT3: Add 30 μl of sample + 30 μl of Rd, incubation for 10 minutes without cleaning, 30 μl of Ra+ 30 μl of Rc incubation for 5 minutes. Wash with 200 μl of washing solution. Finally, add 100 μl of A + 100 μl of B. |
Precision
Sample | RLU | Concentration | Sample | RLU | Concentration |
3.17 | 329,639 | 3.00 | 37.01 | 77,648 | 36.43 |
316,809 | 3.03 | 77,769 | 36.36 | ||
306,416 | 3.19 | 78,584 | 35.85 | ||
310,963 | 3.16 | 74,886 | 38.24 | ||
316,886 | 2.88 | 74,313 | 38.63 | ||
326,138 | 2.92 | 76,182 | 37.38 | ||
314,699 | 3.16 | 77,562 | 36.49 | ||
320,368 | 2.80 | 76,942 | 36.88 | ||
317,900 | 3.13 | 76,563 | 37.13 | ||
319,878 | 2.89 | 79,136 | 35.52 | ||
AVE | 317969.60 | 3.02 | AVE | 76958.50 | 36.89 |
SD | 6733.77 | 0.14 | SD | 1525.12 | 0.99 |
CV | 2.12% | 4.63% | CV | 1.98% | 2.68% |
Limit of detection
Sample | RLU | Concentration | ||
Ag Diluent | 2,154 | 2,156 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
1,986 | 1,978 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
2,051 | 2,223 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
2,208 | 2,064 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
2,035 | 2,045 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
2,124 | 2,062 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
2,104 | 2,110 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
2,065 | 2,056 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
2,289 | 2,001 | 0.04 | 0.02 | |
2,110 | 2,096 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
AVE | 2,096 | 0.02 | ||
SD | 80.22 | 0.01 | ||
AVE+2*SD | 0.04 | |||
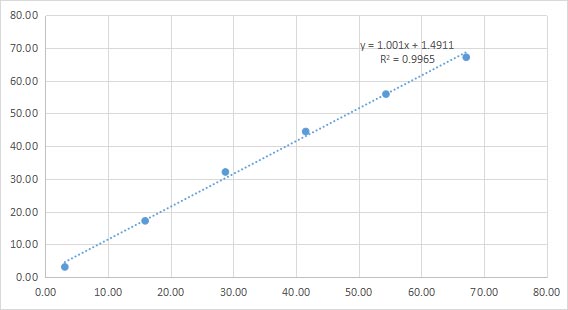
Linear
Sample( pmol/L) | Dilution ratio | Concentration value | Average | ||
67.14 | 1.0 | 66.72 | 67.09 | 67.60 | 67.14 |
54.33 | 0.8 | 56.51 | 53.26 | 57.89 | 55.89 |
41.52 | 0.6 | 45.28 | 44.44 | 43.68 | 44.46 |
28.72 | 0.4 | 31.81 | 32.73 | 31.77 | 32.10 |
15.91 | 0.2 | 16.53 | 17.96 | 17.05 | 17.18 |
3.10 | 0.0 | 3.05 | 3.13 | 3.12 | 3.10 |
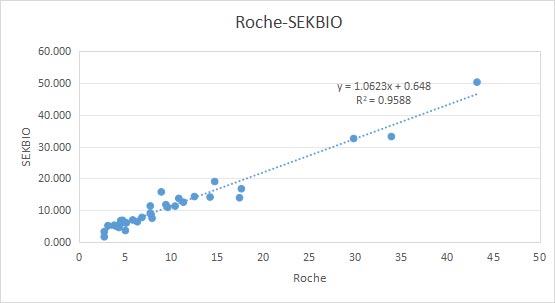
Method Comparison
Reagents Stability
Reagent | Sample( pmol/L) | Average | Deviation |
2-8° | 50.00 | 135,719 | |
10.00 | 434,292 | ||
0.40 | 791,017 | ||
Antigen diluent | 841,178 | ||
random sample | 348,685 | ||
calf serum | 381,680 | ||
37℃ 1d | 50.00 | 134,405 | -0.97% |
10.00 | 424,298 | -2.30% | |
0.40 | 780,909 | -1.28% | |
Antigen diluent | 836,368 | -0.57% | |
random sample | 344,263 | -1.27% | |
calf serum | 373,148 | -2.24% | |
37℃ 4d | 50.00 | 127,883 | -5.77% |
10.00 | 392,923 | -9.53% | |
0.40 | 738,631 | -6.62% | |
Antigen diluent | 777,716 | -7.54% | |
random sample | 329,318 | -5.55% | |
calf serum | 346,663 | -9.17% | |
37℃ 7d | 50.00 | 121,498 | -10.48% |
10.00 | 371,456 | -14.47% | |
0.40 | 709,625 | -10.29% | |
Antigen diluent | 703,179 | -16.41% | |
random sample | 313,072 | -10.21% | |
calf serum | 337,341 | -11.62% |
Calibrator Stability
Reagent | Sample( pmol/L) | Average | Deviation |
2-8℃ | 66.99 | 43,902 | |
37.01 | 74,473 | ||
3.17 | 310,740 | ||
37℃ 1d | 66.99 | 43,667 | -0.53% |
37.01 | 76,993 | 3.38% | |
3.17 | 307,831 | -0.94% | |
37℃ 4d | 66.99 | 43,303 | -1.36% |
37.01 | 75,963 | 2.00% | |
3.17 | 306,706 | -1.30% | |
37℃ 7d | 66.99 | 44,214 | 0.71% |
37.01 | 72,454 | -2.71% | |
3.17 | 305,293 | -1.75% |


















